CELL TO CELL NETWORK
 Connexin:
Gap junctions are also present in many tissues such as retina in which Connexin
43 (Cx43) is mostly present. Connexins are the family of multigene and many
members of this gene is present in the eye. If mutation occurs in the genes
that encodes the several members of Connexin family cause many human diseases.
In-vitro experiments have revealed that Gap junction activity is affected in
the presence of high glucose in pericytes, retinal and microvascular endothelial
cells. It is currently reported that 21 isoforms of connexins is present in
human genome. A change in the gap junction activity and the expression of
Connexin 43 has also been expressed in many diabetic tissues such as diabetic
retina, skin, lens epithelium and kidney. Connexon is a connexin subunits and
assemble in the form of hexamers. Intercellular channels are described as
homotypic and heterotypic. If the molecular composition of two connexins is
same it is known as homotypic, or if the molecular composition is different of
two connexins it is known as heterotypic. In diabetic retinopathy destruction
of the retinal cells causes the retinal lesions in the early stages of diabetic
retinopathy. Connexin maintains the vascular function and GJIC activity for
example, in growth and development. Connexin also modulates the growth signals.
In diabetic condition, the activity of GJIC is reduced which cause the death of
retinal endothelail cells and pericytes. Chronic hyperglycemia associated with
many pathological changes which lead to the breakdown of retinal blood
barriers.
Connexin:
Gap junctions are also present in many tissues such as retina in which Connexin
43 (Cx43) is mostly present. Connexins are the family of multigene and many
members of this gene is present in the eye. If mutation occurs in the genes
that encodes the several members of Connexin family cause many human diseases.
In-vitro experiments have revealed that Gap junction activity is affected in
the presence of high glucose in pericytes, retinal and microvascular endothelial
cells. It is currently reported that 21 isoforms of connexins is present in
human genome. A change in the gap junction activity and the expression of
Connexin 43 has also been expressed in many diabetic tissues such as diabetic
retina, skin, lens epithelium and kidney. Connexon is a connexin subunits and
assemble in the form of hexamers. Intercellular channels are described as
homotypic and heterotypic. If the molecular composition of two connexins is
same it is known as homotypic, or if the molecular composition is different of
two connexins it is known as heterotypic. In diabetic retinopathy destruction
of the retinal cells causes the retinal lesions in the early stages of diabetic
retinopathy. Connexin maintains the vascular function and GJIC activity for
example, in growth and development. Connexin also modulates the growth signals.
In diabetic condition, the activity of GJIC is reduced which cause the death of
retinal endothelail cells and pericytes. Chronic hyperglycemia associated with
many pathological changes which lead to the breakdown of retinal blood
barriers.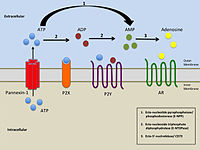 |
| Simplified illustration of extracellular purinergic signalling |
Pannexin:
Pannexins are a huge single membrane channels and pannexin gene family contains
3 members such as panx 1, 2 and 3. Pannexin express in many parts of the
vertebrate body such as nose, ear or lens etc.Pannexin plays a very important
role in the visual system and mainly focused on disease that leading to
blindness. The first condition is Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD) that
condition which leads to the loss of vision. AMD condition is developed when by
the progressive destruction of retinal pig-ment epithelial (RPE) cells in the
macula, which lead to increased intraocular pressure, and the
neovascularization of the subretinal macular region. AMD also cause bleeding
and leakage of the fluids from the eye













0 comments:
Post a Comment
We will get back to you as soon as possible and thanks for the comment.