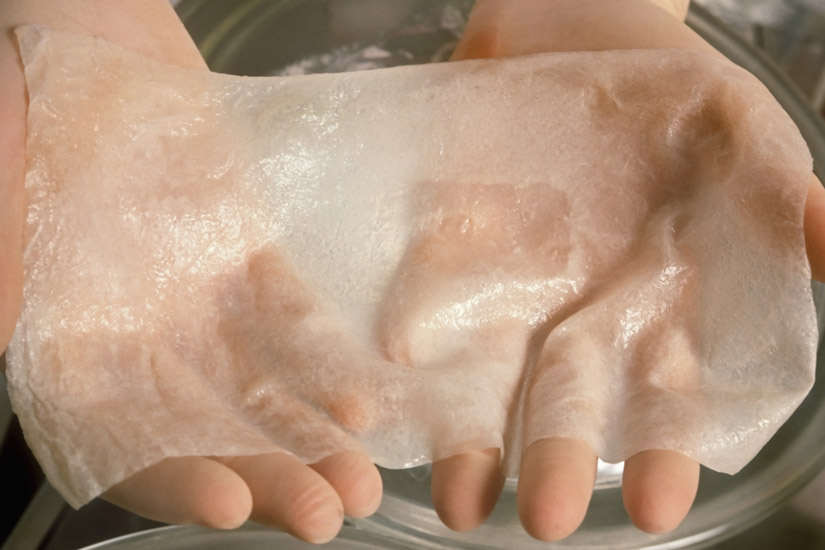

The skin is a complex organ that is difficult to replace
when it is irreversibly damaged by burns, trauma or disease. These are now a
number of commercially available. Skin is our body largest organ. Skin serve as
a external barrier that protects unwanted substances from entering the body.
Skin have three layers; epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis.
In the united states maximum 12,000 deaths annually are
caused by thermal injury. Major contributors to mortality immediately following
severe burn trauma are excessive fluid loss and rampant infection. It’s failure
to achieve skin coverage within three to seven days increase the risk of death.
Since one of the main challenges in treating acute burn
injuries is preventing infection, early excising of the eschar and covering of
the wound becomes critical. Non-viable tissue is removed by initial aggressive
surgical debridement. Many surgical options for covering the wound bed have
been described, although split-thickness skin grafts remain the standard for
the rapid and permanent closure of full-thickness burns.
Significant advances made in the past decades have greatly
improved burns patient care, as such that major future improvements in survival
rates seem to be more difficult. Research into stem cells, grafting,
biomarkers, inflammation control, and rehabilitation will continue to improve
individualized care and create new treatment options for these patients.
Engineering of biologic skin substitutes has progressed over
time from individual applications of skin cells, or biopolymer scaffolds, to
combinations of cells and scaffolds for treatment, healing, and closure of
acute and chronic skin wounds. Skin substitutes may be categorized into three
groups: acellular scaffolds, temporary substitutes containing allogeneic skin
cells, and permanent substitutes containing autologous skin cells.
According to new research if artificial grafting is used
from buffalo and cows is a cheap grafting procedure now a days research is
going on this method in Pakistan in Lahore. So modern technique can prevents
lives which oocur due to burns














0 comments:
Post a Comment
We will get back to you as soon as possible and thanks for the comment.